STUDENT INFORMATION SYSTEM & CLIENT/SERVER APPLICATIONS ON METU-CWIS
The Computer Center in the Middle East Technical University, displaying an intimate effort to catch up with developing information technologies, has had close contact with client/server architectures, Internet technologies, and their natural combination of Intranet technologies recently.
The first significant results of these ongoing studies have been put into practice as a large-scale Student Information System. For the last three years, some student system applications,which were developed with the client/server structure, have been improved further more recently and sophisticated by WEB based Intranet applications. Similar technological renovations are scheduled for The Personnel Information System and others soon.
WEB based access Intranet applications have become one of the most significant subjects of the information sector. The reasons why WEB browsers are becoming more and more widespread on the client side are impressive and obvious. A gradual increase is expected in this general tendency.
In this booklet, you will see how a client/server structure, in which WEB based access is used is practiced in the Student Information System at METU. In the booklet you will initially find the structure, architecture, and problems of the Student Information System. Next, features of the newly developing system and related examples will be presented. Finally, you will have a chance to read the future plans of METU on the subject.
THE SYSTEM DEVELOPED
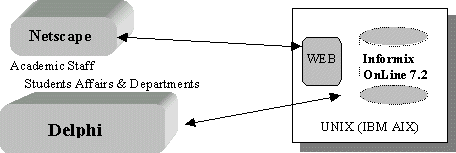 Having
been developed in the last three years, the system comprises a client/server
structure with two parts. Student Information System is located on Informix-OnLine
Dynamic Server 7.2 relational data base in a UNIX (IBM AIX) computer.However,
some modules of access programs are run by the client. Clients can either be
used as programs that are developed by Delphi Client Server 1.0 and that work
on Windows or be used as programs that are written in program language C and
that can work with a Web browser (Netscape Navigator, MS Internet Explorer,
etc.) During access, data are exchanged according to TCP-IP protocol and ANSI-SQL
standards.
Having
been developed in the last three years, the system comprises a client/server
structure with two parts. Student Information System is located on Informix-OnLine
Dynamic Server 7.2 relational data base in a UNIX (IBM AIX) computer.However,
some modules of access programs are run by the client. Clients can either be
used as programs that are developed by Delphi Client Server 1.0 and that work
on Windows or be used as programs that are written in program language C and
that can work with a Web browser (Netscape Navigator, MS Internet Explorer,
etc.) During access, data are exchanged according to TCP-IP protocol and ANSI-SQL
standards.
Thanks to the system, access rights are given to actual owners of the information, which are departments, academic staff, and students. Furthermore, access rights and responsibilities have been rearranged. There are four groups of users:Office of Students Affairs, departments, academic personnel, and students.
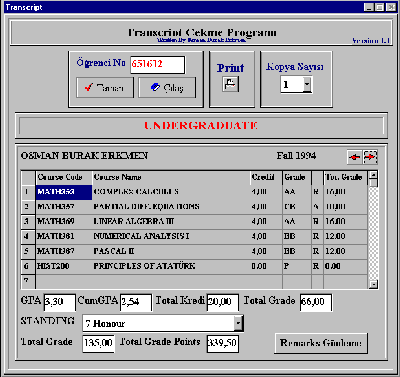
The actual responsibility is held by the Student Center as it was in the traditional system. It is also the responsibility of the Student Center who will access how much information and when. Grading periods, time for the courses to be given to the system in a new semester, preparation of the catalog course information, academic calendar are also under the responsibility of ÖIDB, which has the right to access and update any piece of information with the exception of the above conditions.
The second user group is the academic departments,which control
the correct practice of the academic calendar, which select student advisors and
match them with their students, and which determine the courses to be given in
a new semester, their instructors, schedules and places. With the help of the
newly developed system, departments need not inform ÖIDB of the courses for each
term in written. Departments have the opportunity to open and cut courses through
the programs available in the new system.Thus, departments with their advisors
will follow the academic condition of their students.
The third user group is academic personnel or advisors. Academic personnel grade their students at the end of each term, updating the students' academic average. With the new system, it is possible to grade them with Web Interface (if necessary from all around the world). This opportunity has eliminated the waste of time during completion of optical grading forms.
During registration week, an advisor determines the courses that the student will take according to the needs of the student and then he/she approves the student's registration with the Web browser. The advisor assists the student with other problems too.
The fourth and the last group of users are students. They can only access information, but cannot update it. With the new system, they can easily learn their average grades and academic status. At the beginning of each term, students can see and sign up for the course/courses they want. For the registration, they can use Delphi clients in one of the several PC rooms located on campus. During registration, some important controls are done automatically, for example courses which the student can take according to his academic condition, prerequisite courses, grouping according to departments in large scale courses, information about tuitions, etc.
This new system and application programs enable grade submission system and other processes to be much safer and faster. The system allows people to access information from one source instantly, saving a great amount of time, which is about a week during registration and grading, allowing the yearly academic calendar to have more time. In addition, because students are not using registration forms any more, large amounts of paper is also saved.
The biggest advantage of the new Student Information System is that the computer system of the last user is independent from a certain operating system. The system does not bring an additional task to the last user. Processes are held with the computers that the academic personnel have and with the ones in the labs.
SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE THAT IS PLANNED
METU Computer Center aims to further develop the client server structure and to become independent from brands on both client and server sides. To achieve these, a three-part client server structure is planned.
The current Student Information System can be regarded as suitable for present needs. The most important feature of the system is those 20,000 students and 2,000 academic personnel widely and efficiently use it. On the other hand, the following features can be considered as significant too. The system that is planned to be developed will have three parts, be independent from brands, and be easily compatible.
GATES PITCHES NEW TYPE OF SET-TOP BOX
Microsoft CEO Bill Gates has been meeting with top cable
executives to promote a new digital set-top box design that would connect TVs
and cable systems to provide a variety of two-way interactive programming.
The box would be based on Windows CE software, and Microsoft is suggesting
that rather than collecting software royalties, it would settle for a share
of subscription fees for new services. The company also hopes to sell software
to cable companies' central offices to administer the new services. Other
companies hoping for a slice of the cable set-top box pie are Wink
Communications and Navio, the Netscape Communications spinoff recently
acquired by Oracle Corp.
Wall Street Journal 8 Jul 97
MOTOROLA PULLS THE PLUG ON DRAM CHIPS
With computer memory chip prices spiraling downward,
Motorola is phasing out production of its low-margin DRAM (dynamic
random-access memory) chips by year's end. The company will still crank out
some DRAM chips in the billion-dollar plant now being built in Richmond,
Va -- a joint venture with Siemens -- but once the plant's operating at full
capacity, Motorola will switch over to other types of more profitable chips,
such as flash chips.
Business Week 14 Jul 97
VOICE-CONTROLLED MS WORD
Lernout & Hauspie, a speech technology software vendor,
will introduce a voice-controlled software editor for Microsoft Word in the
fall. Users will be able to select a sentence, underline a group of words, and
change the color and size of a font, all by naturally spoken voice. "It'll make
people give up the mouse," says Lernout & Hauspie's chief technology
officer. The Lernout & Hauspie product uses discrete dictation pathology
software from Kurzweil Applied Intelligence, which it acquired earlier
this year. Kurzweil's artificial intelligence technology allows the software
to prompt users for answers as if they were entering information onto a
form. The initial product will be aimed specifically at pathologists, with
other versions for the legal profession and police reporting to follow.
InfoWorld Electric 17 Jul 97
CREDIT CARD COMPANIES AGREE ON SECURITY STANDARD
Visa and MasterCard say they've agreed on a set of technical
standards for secure electronic transactions, called SET 1.0. The two companies
are already running pilot programs to test the standards in 25 countries, and
hope to introduce the standard to the general market at the end of this year.
"If we work together as an industry, this will go a lot faster," says Visa's
senior VP for I-commerce. The companies hope that the new standard will be in
wide use by next year.
InfoWorld Electric 18 Jul 97
MAC GETS UPGRADE
Apple is launching Mac OS 8, the first major upgrade in six years of
its operating system for Macintosh personal computers. The new system boasts
significantly improved stability as well as a "multi-threading" capability
facilitating the simultaneous execution of various processes. An Apple
executive says, "I feel we have re-established our reputation for quality."
Wall Street Journal 22 Jul 97
WINDOWS 98 TO HAVE FEEL OF WEB BROWSER
Microsoft's next version of its Windows operating system, Windows 98, will allow users to access information wherever it is stored -- whether on a PC, a corporate network, an online service, or the Internet. Industry analyst David Coursey says that Microsoft is "really flexing its muscle...Microsoft must own the desktop PC. It will be absolutely relentless." The new Windows will have the look of a Web browser that can be used to navigate through files by single clicking on highlighted items. It will make it easier to install PC devices (e.g., digital video disc players), make it easier for companies to manage PC networks, and let a user connect a $50-100 TV add-on card to allow a PC to run TV programming from cable and satellite companies.
USA Today 24 Jul 97
Section Source:
EDUCOM Edupage Mailing List<edupage@educom.unc.edu>
HANDWRITING DEMO COLLECTION IN WWW
This collection includes four True Type fonts, three made from children’ handwriting and one a demonstration of a signature / logo font. Also includes information on converting your own handwriting into a font.
http://www.pcworld.com/cgi-bin/shareware?ID=3523
NEW PENTIUM II PROCESSORS TO BE GEARED FOR
SERVERS
(by Judy DeMocker and Andy Santoni, InfoWorld Electric) July 11,1997
Intel is training its biggest guns on server applications, readying Pentium II processors and core-logic chip sets that are tailored to meet server demands. Beginning of August, Intel will announce Pentium II processors geared for low-end workgroup servers, paving the way for systems vendors to release single- and dual-processor systems later this year.
Early next year, Intel will unveil Slot 2 for the high-performance Pentium II processor and the Merced IA-64 processor that will follow.
Slot 2, along with new core-logic chip sets, will allow the Pentium II to scale to four processors and run from a 100-MHz system bus. The Pentium II today runs from a 66-MHz system bus and can scale to only two CPUs.
The new devices will also let the Pentium II access Level 2 cache at the full internal speed of the CPU, not at half the CPU's clock speed.
To tailor the Pentium II to server applications, the processors to be introduced next week will use burst synchronous cache RAM that supports error-correcting code (ECC) on the cache bus, Intel officials confirmed. The devices use existing 233-MHz and 266-MHz Pentium II CPUs.
Until now, ECC was available only for main memory. Pentium II processors have been used in desktop PCs, and have not supported fault-tolerant technology such as ECC in the cache. Earlier this year, Dell and Advanced Logic Research announced server products based on the Pentium II, but most analysts said the market needs hard-and-fast numbers on how the processors perform in servers.
Source: http://www.pcworld.com/cgi-bin/database/body.pl?ID=970711130855
McGRAW HILL WORLD UNIVERSITY
McGraw-Hill World University, the leader in interactive distance education, now offers online degree programs, online courses on Web technology, online certification training, and more. Visit today for sample audio lectures, sample self-tests, and slide shows demonstrations.
Source:
http://www.tipworld.com/arts.cgi?mhwu
Section Source: TipWorld™
http://www.tipworld.com
DEEP BLUE TEAM AWARDED
(by Tom Karlo July 29, 1997)
IBM's Deep Blue team received the $100,000 Fredkin Prize for Computer Chess today in recognition of their victory over world chess champion Garry Kasparov this May. Dr. Feng Hsiung Hsu, who designed Deep Blue's chess processing chip, Dr. Murray Campbell, who programmed Deep Blue, and Dr. Joseph Hoane, an expert in parallelism who worked on the systems performance, received the prize.
The prize was awarded by Carnegie Mellon University, where it was established by computer science professor Edward Fredkin 17 years ago to encourage research in computer chess. The prize originally consisted of three separate awards: $5,000 for the first team to develop a machine achieving master status, $10,000 for the first group to create a machine of international master status, and $100,000 for the first team to develop a computer capable of beating the world chess champion.
The first milestone was reached by a pair of scientists from Bell Laboratories in 1981, while the second award was given in 1988 to five Carnegie Mellon graduate students who built Deep Thought. Two of those researchers, Hsu and Campbell, participated in the Deep Blue team receiving today's award.
Deep Blue lost an earlier match against Kasparov before beating him this year. The difference, according to Murray, wasn't so much raw computing power as the efficiency and effectiveness of the computer's chess strategy.
IBM is now looking to convert the research done on Deep Blue into more mundane but profitable applications. And now that the team has beat the world champion, it's looking for some new avenues of research. "We're definitely going to spend some more of our time now on real-world applications" said Murray. Among the applications under consideration are such complex, compute-intensive tasks as molecular dynamics, financial analysis, and data mining.
For today, however, the team is happy to receive their award. "Ever since computers have been around people have been thinking about how to program a computer to play chess," noted Murray. "The victory by Deep Blue is something that's only going to happen once." Today's event marks the retirement of the Fredkin Award.
Source: http://www.news.com/News/Item/0,4,12920,00.html?owv
Section Source: http://www.news.com/